Oral Exam Prompt: Brachytherapy, Radiation Protection and Radiobiology 1
What types of imaging are used to evaluate this disease?
Why is iodine used instead of another radionuclide?
What is I-131's half-life and mode of decay?
Is this an in-patient or out-patient procedure? How is that determined?
What governing body regulates this administration and what documents are used for guidance?
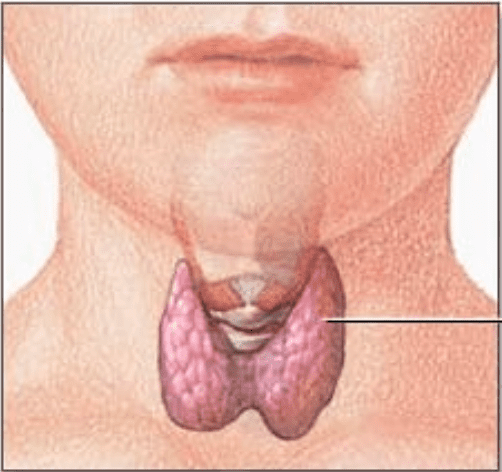
What is this organ?
Thyroid gland


What are common treatments for cancers of this organ?
Thyroidectomy (removal of thyroid) followed by treatment with iodine 131 is most common.
What types of imaging are used to evaluate this disease?
Ultrasound is used to asses nodule size and can visualize microcalcifications indicative of thyroid cancer.
I-123 SPECT imaging can assess thyroid function and potential disease spread.
Why is iodine used instead of another radionuclide?
Radioactive iodine is ideal because thyroid cells are the only cells in the body that actively absorb iodine. Absorbed iodine is incorporated into thyroid hormones.
What is I-131's half-life and mode of decay?
Half-life = 8 days
Decays via beta decay to an excited state of xenon. Xenon subsequently returns to ground state via gamma emission.
Is this an in-patient or out-patient procedure? How is that determined?
I-131 therapy is most often an out-patient procedure but may be an inpatient procedure if the expected dose to another individual will exceed 5mSv.
For I-131 a patient may be released if he/she meets any of the following criteria:
- Administered activity was less than 33mCi
- Dose rate measured at 1 meter from the patient is less than 0.07mSv/hr
- A patient specific dose calculation indicates dose to other individuals will be less than 5mSv.
- Calculation may include effective half-life, organ shielding, living conditions, and other factors.
What governing body regulates this administration and what documents are used for guidance?
This is governed by NRC 10 CFR 35.75 but may be superseded by state law in agreement states.
The NRC has also released a guidance document (NRC Regulatory Guide 8.39) which list release criteria in terms of administered activity, dose rate measured at 1 meter from the patient, and dose calculation methods.
Learn more about I-131 thyroid therapy here (internal link).
